Component structure¶
A MACH component is in it's bare minimum a Terraform module.
Other then the Terraform configuration, a component might include a serverless function for custom logic to be executed runtime.
Deployment process¶
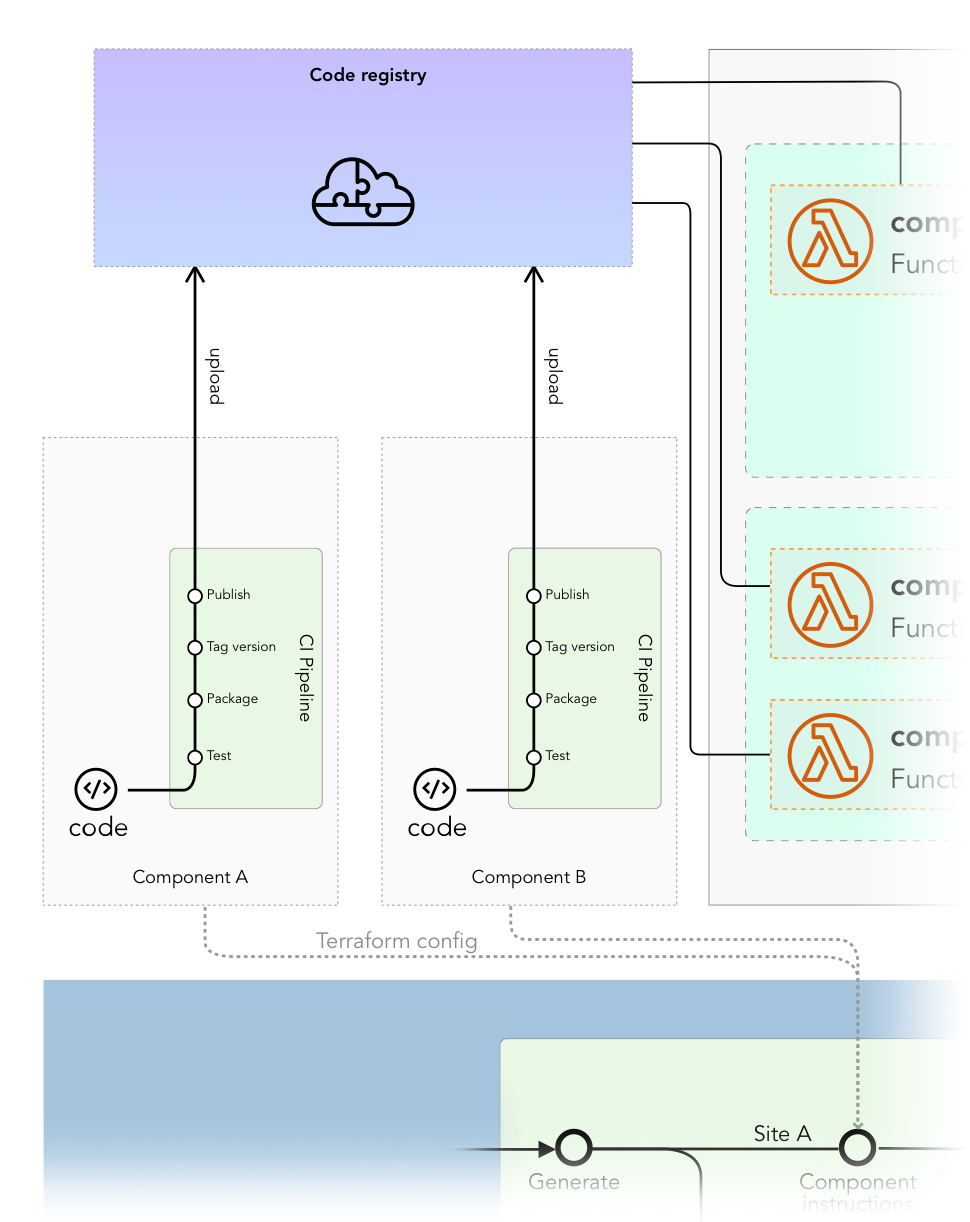
The deployment of a full-fledged component typically flows through the following steps:
- In case of a serverless function it is built, packaged and uploaded to a shared resources all environments and sites can access.
Note: at this point, no actual deployment is made; the function doesn't run yet. - At the moment the MACH composer deploys a site's Terraform configuration, it uses the component's Terraform configuration to make the necessary modifications to the resources.
For example: create the function app instance, necessary routing, etc. - MACH composer will use the packaged function (from step 1) to deploy the function itself
Simple components
Not all components need to be a serverless function. A component might be just a set of Terraform instructions to, for example, create a custom product type in commercetools.
In that case, step 1 and 3 will be skipped.
Zooming in on the main diagram, you'll see the steps illustrated.
Terraform module¶
The component must be able to instruct MACH wat resources to create in the cloud infrastructure. This is done by providing the necessary Terraform module files in the component.
A good practise usually is to place all Terraform files in a single terraform/ directory and reference that in your MACH configuration.
Required variables¶
MACH expects each component to have a certain set of variables defined.
What variables it needs to have defined is controlled by the integrations setting.
If integrations is set to an empty list [], no variables will be needed.
An example of a component that takes no variables could be a component that creates custom product types in commercetools. This component operates with the same Terraform commercetools provider which is configured for the correct project already, so no additional information will be needed in the Terraform module itself.
Integrations¶
By defining a set of integrations in the component definitions, MACH knows what variables need to be passed on to the components.
This way the components don't need to define all possible variables a component might have.
Available integrations are:
awsazurecommercetoolssentrycontentfulamplience
By default, integrations are set on the given cloud provider. So when no integrations defintion is given, it defaults to ['aws'] in case of an AWS deployment.
Non-cloud components
As an example; you might have a component defining some custom commercetools product types. No further cloud infrastructure is needed.
In this case, that component will have integrations: ['commeretools'] and MACH won't pass any of the cloud-specific variables.
cloud integration¶
The following variables are expected in case of either aws or azure.
variable "component_version" {
type = string
description = "Version to deploy"
}
variable "environment" {
type = string
description = "Specify what environment it's in (e.g. `test` or `production`)"
}
variable "site" {
type = string
description = "Identifier of the site"
}
variable "variables" {
type = map(string)
description = "Generic way to pass variables to components."
}
variable "secrets" {
type = map(string)
description = "Map of secret values. Can be placed in a key vault."
}
Cloud specific variables
See AWS variables and Azure variables for cloud-specific variables that a component needs in addition to the base set.
commercetools¶
The following variable is given when commercetools integration is defined.
variable "ct_project_key" {
type = string
description = "commercetools project key"
}
variable "ct_api_url" {
type = string
description = "commercetools API URL"
}
variable "ct_auth_url" {
type = string
description = "commercetools Auth URL"
}
variable "ct_stores" {
type = map(object({
key = string
variables = map(string)
secrets = map(string)
}))
default = {}
}
sentry¶
The following variable is given when sentry integration is defined.
variable "sentry_dsn" {
type = string
default = ""
description = "Sentry DSN - only when Sentry is configured"
}
contentful¶
The following variable is given when contentful integration is defined.
variable "contentful_space_id" {
type = string
description = "Contentful Space ID"
}
amplience¶
The following variable is given when amplience integration is defined.
variable "amplience_client_id" {
type = string
description = "Amplience client id"
}
variable "amplience_client_secret" {
type = string
description = "Amplience client secret"
}
variable "amplience_hub_id" {
type = string
description = "Amplience hub id"
}
Serverless function¶
The component might contain code for a serverless function to run on the cloud provider.
What kind of language/runtime is used for that is irrelevant to MACH. Two things the component needs to contain:
- Build/deploy script to build, package and upload the serverless function to a repository
- A Terraform configuration for the serverless function
Cloud provider specifics¶
A component is always tailored for a specific cloud provider.
Continue for details about the specifics: