Deploy using Azure DevOps pipelines¶
This section will describe how to set up your CI/CD pipeline using DevOps including some examples.
Azure DevOps documentation is no longer maintained
While it is perfectly possible to implement MACH composer in an Azure DevOps pipeline, we will not be updating its documentation anymore, as Azure DevOps seems to be on its way out. We will be focusing on GitHub Actions instead.
For a current implementation of a GitHub CI/CD flow, please see the GitHub CI/CD documentation of MACH composer.
MACH stack deployment¶
How to set up the deployment process for your MACH configuration.
Providing credentials¶
The pipeline must be able to;
1. Create KeyVault¶
Start off by creating a KeyVault in which we can store credentials needed in the pipeline
$ az keyvault create --name myprefix-devops-secrets --resource-group my-shared-we-rg
2. Azure service connection¶
We need to provide access to Azure using a service connection.
The pipeline needs this to be able to access the KeyVault to pull in other credentials with.
- Go to your Project settings
- Choose Pipelines > Service connections
- Choose 'Azure Resource Manager'
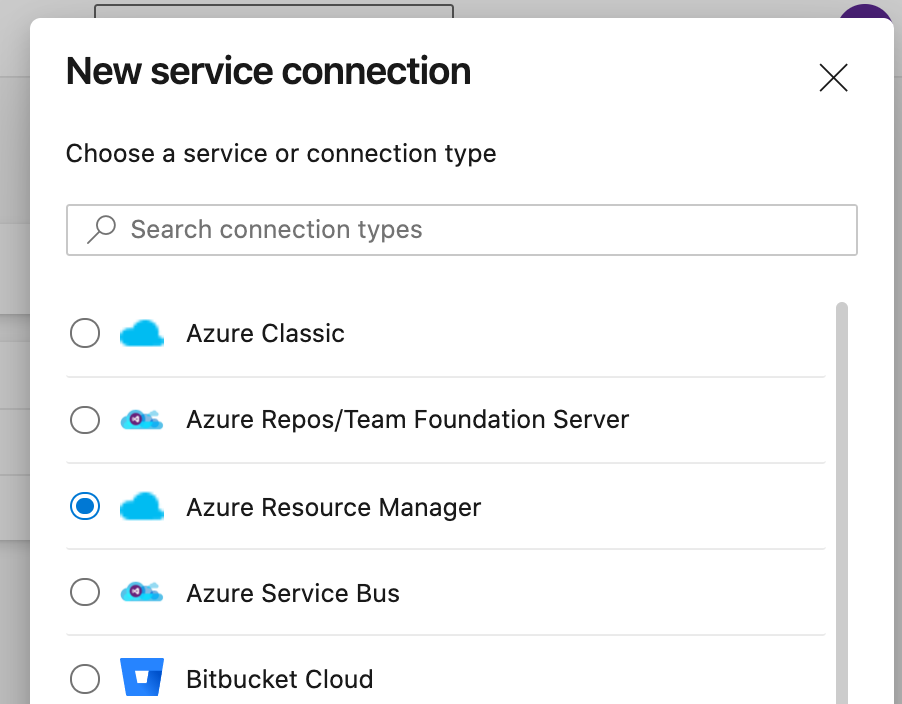
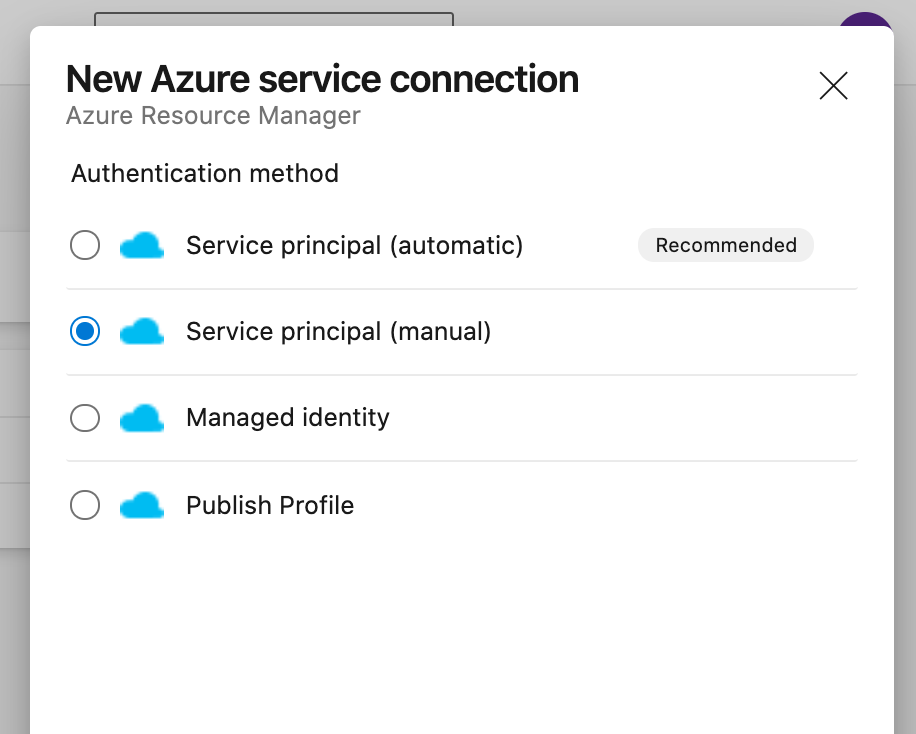
And then 'Service principle (automatic)' or 'manual' depending on your situation and permissions. - Enter the credentials needed.
The name given in Service connection name will be used later in the pipeline.
3. MACH docker image¶
We need to configure a Docker Registry service connection for the pipeline to use the MACH docker image.
- Go to your Project settings
- Choose Pipelines > Service connections
- Choose 'Docker Registry'
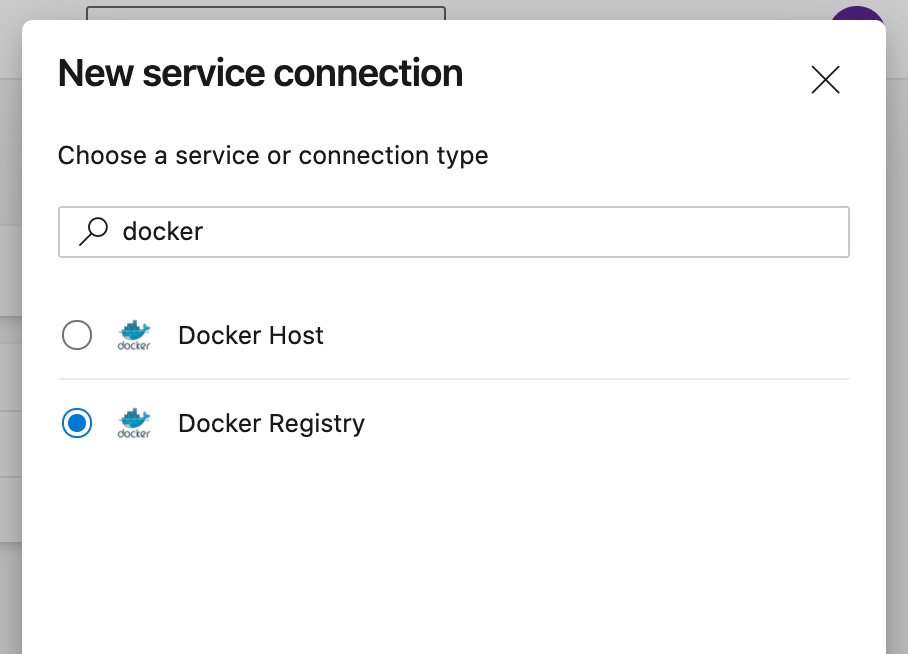
- Enter
https://docker.pkg.github.comas Docker registry
The name given in 'Service connection name' will be used later in the pipeline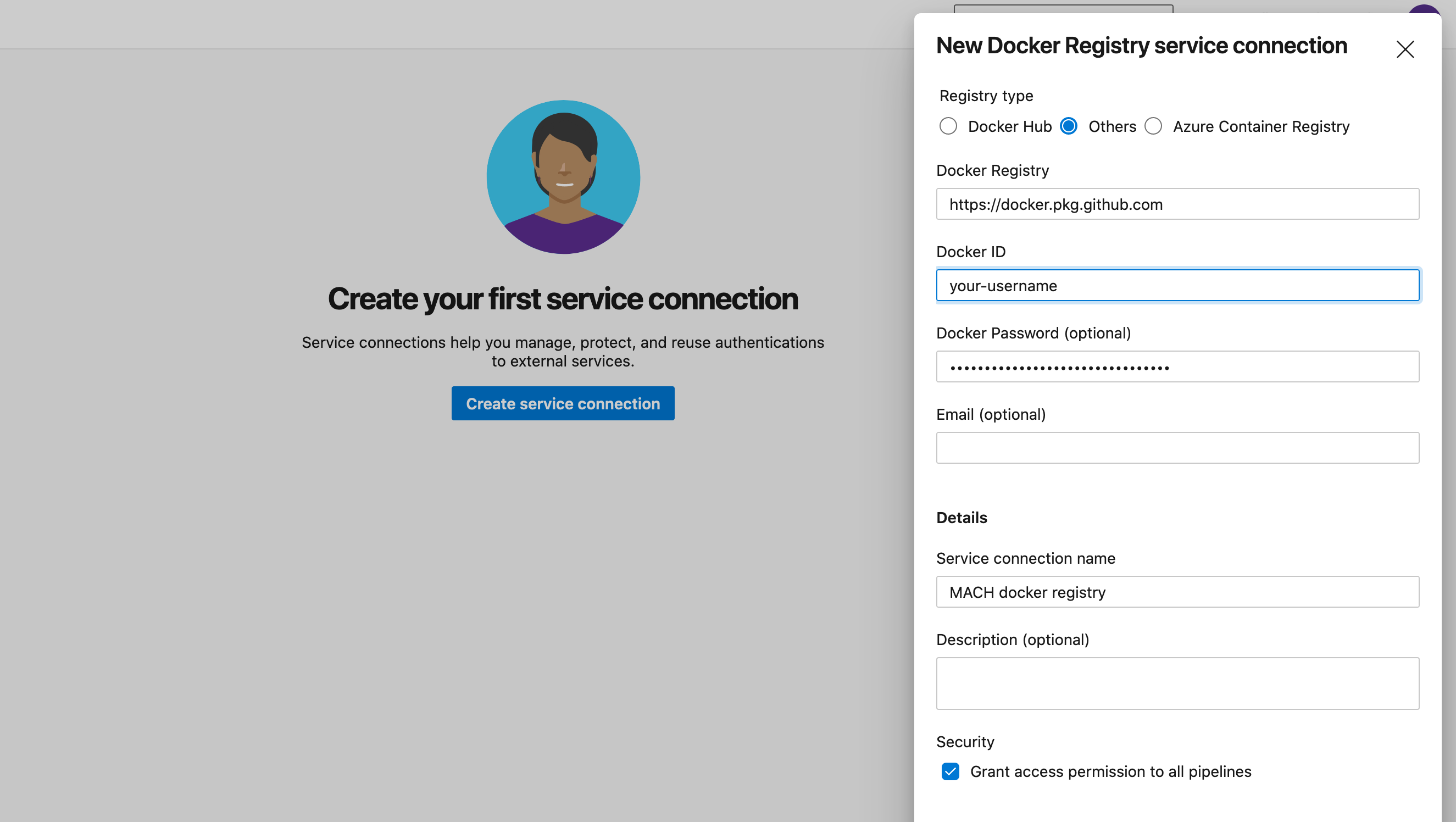
4. Component repositories¶
- Generate an SSH key pair. Instructions.
- Add the public key to the SSH public keys of a user that has (at least read-) access to the component repositories.
- Store the private key in the KeyVault.
$ az keyvault secret set --name "SSHPrivateKey" --value "$(cat id_rsa)" --vault-name my-devops-secrets
5. Provide SP credentials¶
MACH composer needs to be able to log in to Azure to manage the resources.
We need to be able to provide the following environment variables:
ARM_CLIENT_IDARM_CLIENT_SECRETARM_SUBSCRIPTION_IDARM_TENANT_ID
In this case, we're going to store the ARM_CLIENT_ID and ARM_CLIENT_SECRET
in the KeyVault, so we don't have to hard code it in the pipeline.
$ az keyvault secret set --name "DevOpsClientID" --value "..." --vault-name my-devops-secrets
$ az keyvault secret set --name "DevOpsClientSecret" --value "..." --vault-name my-devops-secrets
Example¶
trigger:
- master
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
variables:
SP_TENANT_ID: <your-tenant-id>
SP_SUBSCRIPTION_ID: <your-subscription-id>
steps:
- task: AzureCLI@2
displayName: Fetch SSH private key
inputs:
azureSubscription: <service-connection-name>
scriptType: bash
scriptLocation: inlineScript
inlineScript: 'az keyvault secret download --vault-name myprefix-devops-secrets -n SSHPrivateKey -f id_rsa'
- task: AzureKeyVault@1
displayName: Get secrets
inputs:
azureSubscription: <service-connection-name>
KeyVaultName: myprefix-devops-secrets
SecretsFilter: 'DevOpsClientID,DevOpsClientSecret'
RunAsPreJob: true
- script: |
mkdir -p ssh
mv id_rsa ssh/id_rsa
echo "" >> ssh/id_rsa
chmod 600 ssh/id_rsa
ssh-keyscan ssh.dev.azure.com > ssh/known_hosts
displayName: Prepare credentials
- task: Docker@2
inputs:
containerRegistry: '<docker-service-connection-name>'
command: 'login'
- script: |
docker run --rm \
--volume $(pwd)/ssh:/root/.ssh \
--volume $(pwd):/code \
-e ARM_CLIENT_ID=$(DevOpsClientID) \
-e ARM_CLIENT_SECRET=$(DevOpsClientSecret) \
-e ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID=$SP_SUBSCRIPTION_ID \
-e ARM_TENANT_ID=$SP_TENANT_ID \
docker.pkg.github.com/mach-composer/mach-composer-cli/mach:2.0.0 \
apply --with-sp-login --auto-approve -f main.yml
displayName: Apply
Component deployment¶
For the component CI pipeline we need to be able to test, package and upload the function app ZIP file.
Setup Azure service connection¶
Just as in the step for setting up the MACH stack, we need to add an Azure service connection so that the pipeline can upload the function apps to the storage account.
The Service connection name will be used later in the pipeline.
Example¶
Example DevOps CI configuration.
See the Components deployment section for examples of the package/upload script used here.
trigger:
- master
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
steps:
- script: |
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | gpg --dearmor > microsoft.gpg
sudo mv microsoft.gpg /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/microsoft.gpg
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/microsoft-ubuntu-$(lsb_release -cs)-prod $(lsb_release -cs) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/dotnetdev.list'
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install azure-functions-core-tools-3
displayName: Install core tools
- task: UsePythonVersion@0
inputs:
versionSpec: '3.8'
displayName: 'Use Python 3.8'
- script: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
displayName: 'Install dependencies'
- script: |
pip install pytest pytest-azurepipelines
pytest
displayName: 'Test'
- script: ./azure_package.sh package
displayName: Package
- task: AzureCLI@2
displayName: Upload
inputs:
azureSubscription: '<azure-service-connection>'
scriptType: bash
scriptPath: ./azure_package.sh
arguments: upload
Note
In the example, you'll see a script to install the Azure functions core tools.
The functions core tools cannot be injected in the pipeline easier because of a still unresolved bug.
See: https://github.com/Azure/azure-functions-core-tools/issues/1899